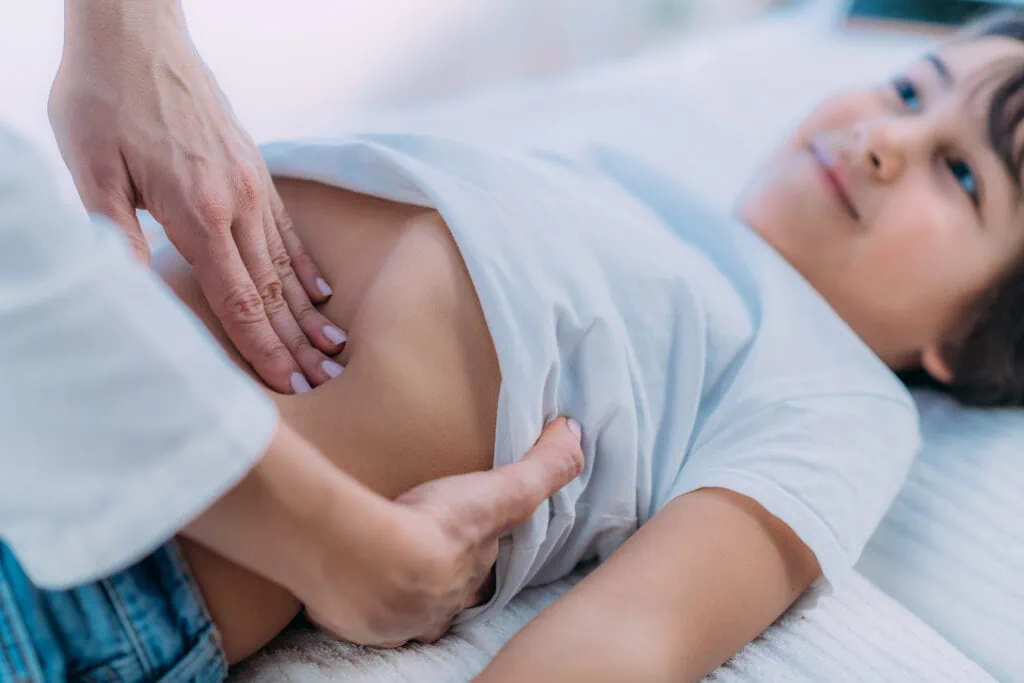
Appearance:
Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Risk of infection:
Vomiting and diarrhea are often very contagious.
Measures:
- Giving enough to drink by offering frequent sips of liquid
→ Sweetened or unsweetened tea, water with dextrose. For infants, infant milk or breast milk. If necessary, electrolyte solutions can help (Oralpädon, Normalytoral, Elotrans) or the WHO one-third solution (1/3 orange juice, 1/3 black tea, 1/3 tap water, 1 pinch of salt and a soup spoon of dextrose) per liter - cold in small quantities. - Relieve abdominal pain with a hot water bottle
- Rest
- No personal contact with immunocompromised persons
- Rusks, pretzel sticks, bananas, light food (low fat) in small amounts (If the child has no appetite, there is no need to worry about this. Drinking is currently more important)
- Avoid fruit juices, cow's milk, or hard-to-digest foods for short periods of time
- Careful hand hygiene
Report to docter if:
- bloody vomit or bloody diarrhea
- if your child refuses fluids or urinates less than 3x/day
- if the child is weak and apathetic even without fever
- as long as none of these criteria are met, no medication is usually necessary